State of encrypted traffic
Hackers have expanded their craft to use SSL traffic to obfuscate their attacks and malware from security systems.
- 97% of surveyed enterprises are seeing an increase in encrypted web traffic.
- 130% increase in threats using TLS/SSL connections in 2016 over 2014.
- 41% of malware is hidden in SSL traffic.
- 80% of those surveyed were victims of a cyber attack.
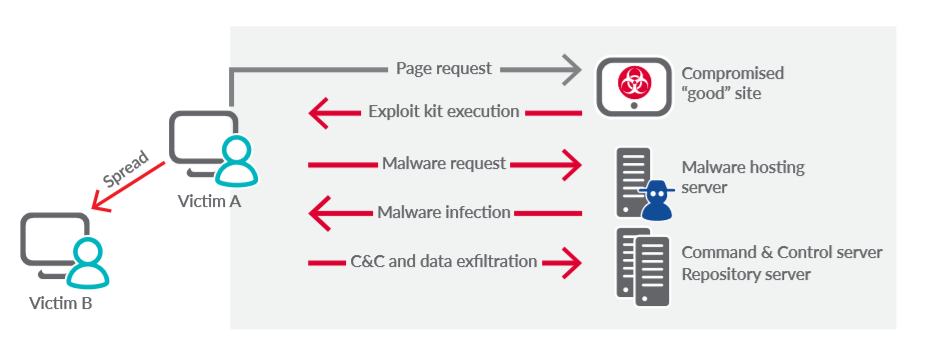
Understanding the malicious use of encryption
- Page visit: User machine (victim A) visits a compromised good site.
- Exploit Kit Execution: As the web content is served to the client, a small piece of software is downloaded to the user’s device where a sequence of commands is executed to exploit software vulnerabilities ont he client machine.
- Malware Request: Once the exploit kit operator gets control of that machine, a request command is made to a malware hosting website that delivers the malware.
Encryption can be implemented at any phase of an attack
- Malware Infection: Victim A now has malware installed.
- C&C: The malware communicates back to a Command and Control infrastructure for more instructions.
- Data Exfiltration: Data from Victim A’s machine is copied to an external server for processing.
- Victim B: Attackers often elevate their access rights at this stage allowing them to move laterally within the network and infect other endpoints.
- Encryption: The new reality is that encryption can be implemented at any phase of this attack to evade detection.
The challenges of encrypted traffic
Three common barriers for not inspecting SSL traffic
- 47% of lacking of enabling security tools
- 45% of insufficient resources
- 45% of performance degradation
Performance impact is a big concern
- Performance penalty on a security system when SSL inspection is active can be as high as 81%.
- 61% say lack of performance is a concern for organizations that don’t decrypt SSL traffic.
- 83% say decryption results in some type of degradation within organizations currently decrypting and inspecting SSL traffic.
The sonicWall solution
The SonicWall solution: Breaking the malware cycle operating inside encrypted traffic
- SonicWall protects endpoint systems inside or outside the firewall perimeter from visiting inappropriate, illegal and malicious URLs with the firewall’s Web Content Filtering and Enforced Content Filtering Client.
- The unique SonicWall Deep Packet Inspection of SSL (DPI-SSL) technology decrypts encrypted internet traffic between clients and web servers.
- The SonicWall Intrusion Prevention Service scans the unencrypted traffic to protect against application vulnerabilities as well as worms, Trojans, and peer-to-peer, spyware and backdoor exploits.
- SonicWall threat prevention security services, including Gateway AntiVirus, Cloud Anti-Virus, Botnet and GeoIP Filtering and third-party threat information, further break the malware infection cycle.
- SonicWall Capture ATP, a multi-engine sandbox platform, executes and examines suspicious files to discover and stop zero-day threats.

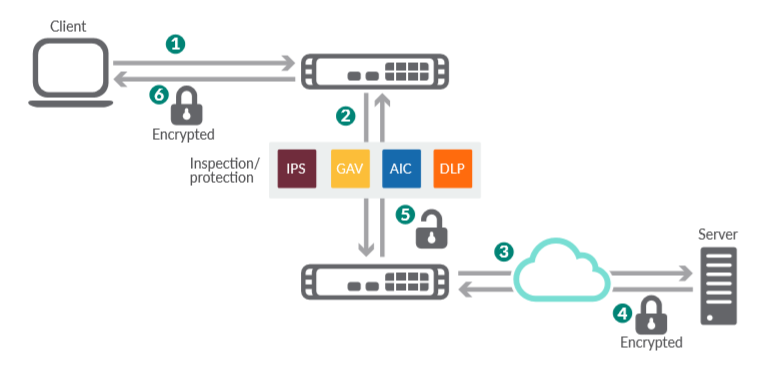
The SonicWall Solution: How DPI-SSL decrypts and inspects encrypted traffic
- Client initiates SSL/TLS handshake with server.
- NGFW intercepts request and establishes session using its own certificate in place of server.
- NGFW initiates SSL/TLS handshake with server on behalf of client using admin-defined SSL/TLS certificate.
- Server completes handshake and builds a secure tunnel between itself and NGFW.
- NGFW decrypts and inspects all traffic coming from or going to client for encrypted threats.
- NGFW re-encrypts safe traffic, sends along to client and blocks encrypted threats.
 The customer outcomes
The customer outcomes
- Gain visibility into SSL/TLS encrypted traffic.
- Block malware downloads hiding inside encrypted traffic.
- Thwart command and control communications and data exfiltration.
- Enhance security, application control and data leak prevention capabilities.
- Maintain highest level of network and resource quality of service and availability as the system load increases without performance problems.

